Upper Tail Probability Table
Because of the lack of symmetry of the chi-square distribution separate tables are provided for the upper and lower tails of the distribution. Are used to determine null hypothesis.
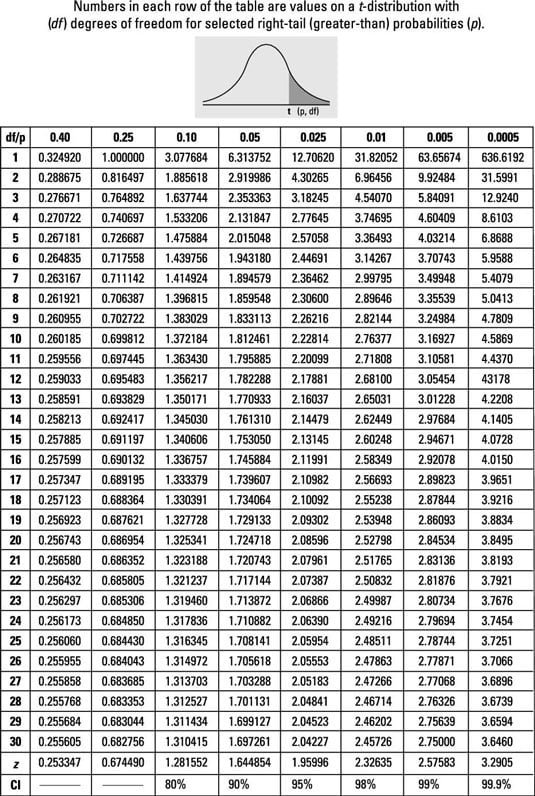
How To Use The T Table To Solve Statistics Problems Dummies
The complete table of critical values of Z for upper lower and two-tailed tests can be found in the table of Z values to the right in Other Resources.

. Probability Distributions of Discrete Random Variables. There are also online sites available. Consequently the p-value measures the compatibility of the data with the.
I attach my own solution PDF 33K to the problem in case it is of interest. In terms of a random experiment this is nothing but randomly selecting a sample of size 1 from a set of numbers which are mutually exclusive outcomes. In probability theory and statistics kurtosis from Greek.
As its over the upper inner fence but not over the upper outer fence its considered a mild outlier. Incidentally I would give this problem four stars rather than three --took me days to get it clear. The revised second edition includes new sections on extreme value copulas tail dependence and quasi-copulas.
T-Distribution Table One Tail and Two-Tails Chi Squared Table Right Tail Z-table Right of Curve or Left. Ex ante the probability of selecting that point is zero. Only one point 1699 is an outlier because it lies outside the fences.
Plot the upper and lower fences on a box plot. For upper-tail one-sided tests the. The p-value or the observed level of significance is the smallest level of significance at which you can reject the null hypothesis assuming the null hypothesis is true.
Upper Probability is 031. An overview of all model specifications and adjustments is provided in Table 2. The only prerequisite is an upper level undergraduate course in probability and mathematical statistics although some familiarity with nonparametric statistics would be useful.
The possibilities are HHTT HTHT HTTH TTHH THHT THTH where H represents a head and T represents a tail. In Expression enter 1-K1. For an upper-tailed test you need to subtract this probability from 1.
The forecast exercise thus features three competing models alongside 18 variants of UCQR governed by the respective prior treatment of the scale parameter and ex post adjustment of quantile estimates. Their name introduced by applied mathematician Abe Sklar in 1959 comes from the. K1 contains the probability that the test statistic assumes a value equal to or greater than that value actually observed based on your sample under Ho.
The following examples show how to do the calculation on the TI-8384 and with R. You then type in the lower limit upper limit mean standard deviation in. In probability theory and statistics a copula is a multivariate cumulative distribution function for which the marginal probability distribution of each variable is uniform on the interval 0 1.
Cont If you want 196 from 095 you have to make use of the fact that the normal distribution is symmetric and divide the amount youre ignoring in half to get just the upper tail ignored. Will calculate the probability for a normal curve including Excel and the TI-8384. Here the sample space is 123456 and we can think of many different.
Stnormppf1-1-0952 1959963984540054 - Basic statistics yes but I just wanted to make it explicit. A normal probability plot. T Value Right Tailed is 0031.
Which numerical summary would you like to calculate for each group. For a 95 confidence interval the area in each tail is equal to 0052 0025. Not necessarily statistically but it makes outliers easier to spot.
Knowledge of measure-theoretic probability is not required. The right tail has positive values while the left tail has negative ones. You can also think about the p-value as the total area of the region of rejection.
Copulas are used to describemodel the dependence inter-correlation between random variables. Remember that in a one-tailed test the regi. With a comparatively stable upper tail of the distribution.
A test statistic with ν degrees of freedom is computed from the data. But there is a more specialized type of plot you can create called a normal probability plot. The graph of the normal probability distribution is a bell-shaped curve as shown in Figure 73The constants μ and σ 2 are the parameters.
The p-value is the probability that the data could deviate from the null hypothesis as much as they did or more. It helps to calculate the value from the Z table very quickly in real-time. PTS 1785 09629.
The binomial coefficient multiplies the probability of one of these possibilities which is 12²12² 116 for a fair coin by the number of ways the outcome may be achieved for a total probability of 616. Ex post the probability must have been greater than zero because it happened. The command on the TI-8384 is in the DISTR menu and is normalcdf.
In the image below the upper right data item is clearly out of line with the rest of the data meaning. For a large-sample runs test where n 1 10 and n 2 10 the test statistic is compared to a standard normal table. A typical example for a discrete random variable D is the result of a dice roll.
Choose Calc Calculator. The value z representing the point on the standard normal density curve such that the probability of observing a value greater than z is equal to p is known as the upper p critical value of the standard normal. How to Use This Table This table contains the critical values of the chi-square distribution.
However null hypothesis is the area between right and left tails. That is at the 5 significance level a test statistic with an absolute value greater than 196 indicates non-randomness. In Store result in variable enter K2.
Namely μ is the population true mean or expected value of the subject phenomenon characterized by the continuous random variable X and σ 2 is the population true variance characterized by the continuous random variable X. κυρτός kyrtos or kurtos meaning curved arching is a measure of the tailedness of the probability distribution of a real-valued random variableLike skewness kurtosis describes the shape of a probability distribution and there are different ways of quantifying it for a theoretical distribution and corresponding ways.
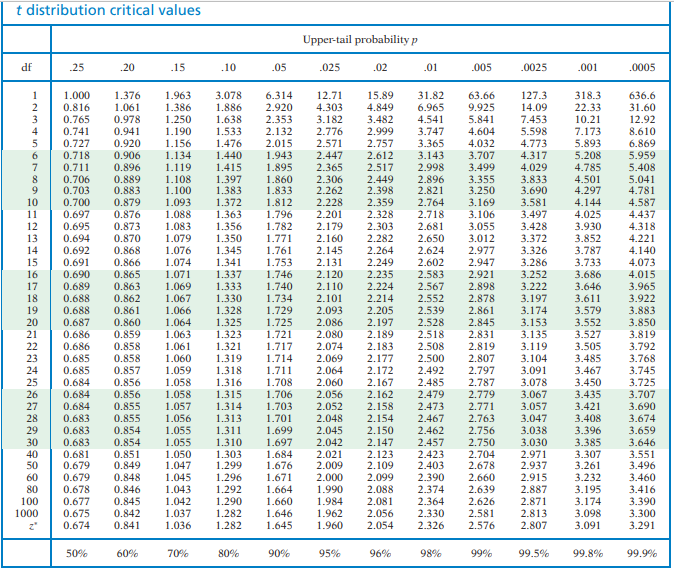
T Distribution Critical Values Upper Tail Probability Chegg Com
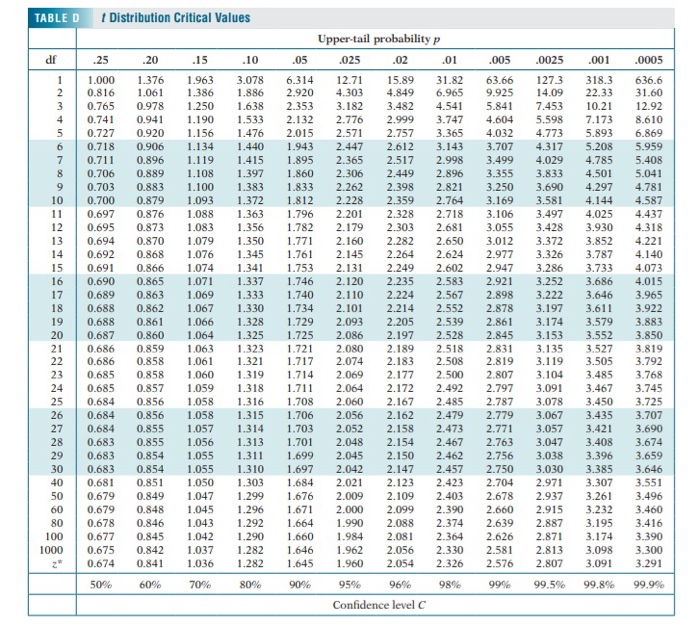
Solved My Notes Ask Your Teacher 06 Points Mintrosat97 Chegg Com
No comments for "Upper Tail Probability Table"
Post a Comment